Rucete ✏ Chemistry In a Nutshell
Quantum numbers
1. n (Principal(Shell) quantum number)
The energy level contained within an atom
There are 1-7 energy levels
The shell moves away from the nucleus as 'n' increases, and the electron gains energy.
The maximum electrons that can be accommodated in an electronic shell: 2n²
--> K shell = period 1 atoms ex) H, He (n=1) 1n² = 2
L shell ex) Li, Be (n=2) 2n² = 8
M shell ex) Na. Mg (n=3) 3n² = 18
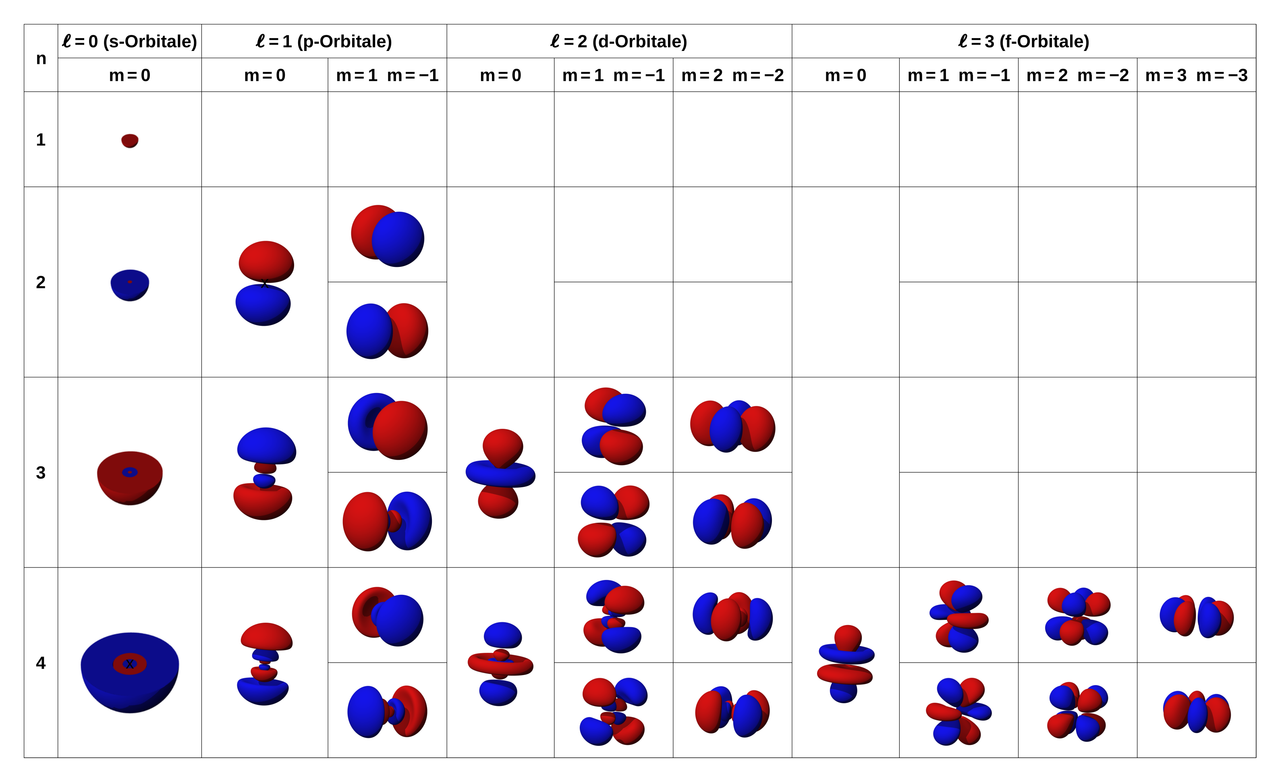
2. ℓ (Momentum(Subshell) quantum number)
Describes the orbital shape
One orbital can only have up to two electrons
'ℓ' has the value of (n - 1)
-ℓ = 0 (s orbital = spherical)
-ℓ = 1 (p orbital = dumbbell shape)
-ℓ = 2 (d orbital = cloverleaf shape)
-ℓ = 3 (f orbital)
3. ml (Magnetic quantum number)
Describes the orbital's direction or orientation in space
s : 1 orbital -> 0
p : possible to 3 orbital -> Px, Py, Pz ; -1. 0. 1
d : possible to 5 orbital -> dz2, dxz, dyz, dxy, dx^2-y^2 ; -2, -1, 0, 1, 2
f : possible to 7 orbital -> -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3
4, ms (Spin quantum number)
Describes the electron's spin.
An electron in the same orbital has a spin in the opposite direction.
The spin has clockwise(+1/2) or counterclockwise(-1/2)
Tags:
Chemistry in a nutshell