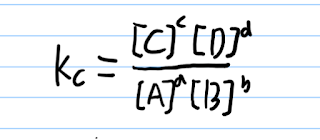The equilibrium constant (Kc)
Rucete Chemistry In a Nutshell
Any mechanism of equilibrium has a particular ratio of reactants to products. This ratio can be written as a mathematical formula, called an expression of equilibrium, and is constant.
Any temperature, normally 25°C.
The equation is:
For example,
The concentration of all solids is related to their density. It is also a constant and is built into the value of Kc. Therefore, we keep all the solids out of the expressions of equilibrium.
In addition, water is left out of equilibrium constants if the reaction takes place in an aqueous environment. In this case, the water is so much higher that its concentration is hardly changed by the reaction and is incorporated into the Kc value.
The constant equilibrium of the reaction tells the chemist whether the reaction favors the reactants or the products. If Kc is high, the product will be favored by the reaction. A small Kc (less than 0.1) means that only a small proportion of the product will be made more. The term also demonstrates how changing the concentration of one reagent can be more efficient than changing the concentration of one of the other reagents.
Tags:
Chemistry in a nutshell